Developing the first
European IMU
for Space Navigation
Developing the first European IMU for Space Navigation
About EURISA
EURISA aims at developing the first European cost-effective and performant IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) based on fiber-optic gyroscopes and quartz accelerometers for future space missions.
EURISA involves four major actors of the European space ecosystem and research institutes: Airbus Defence & Space, ETH Zurich, DLR Bremen and Exail (formerly iXblue).
EURISA will contribute to European independence and sovereignty in space for future missions and exploration.
EURISA is a Horizon 2020 projects, funded for 3.5 years by the European Union (under grant agreement No 101004205).

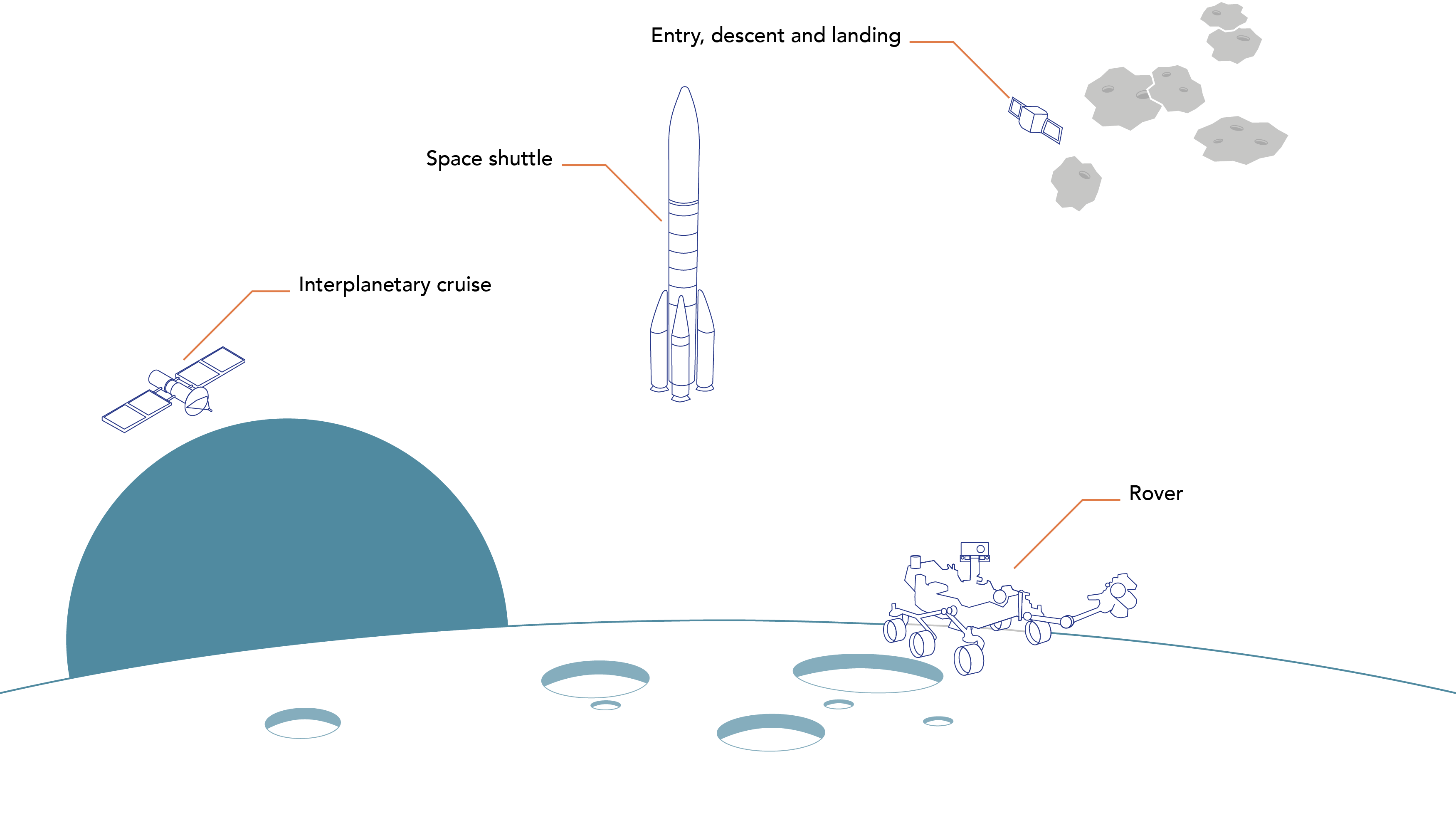
What's an IMU?
An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is a device that combines input from several different sensors types in order to accurately output a movement.
It is composed of 3 Accelerometers measuring velocity and acceleration and 3 Gyroscopes measuring rotation and rotational rate
In space, IMUs are used on spacecrafts, space probes, landers, rover or satellites.
Project duration
January 2021 to
June 2024
Consortium
4 partners from
3 countries
Goal
A European IMU
for space
Press releases

Eurisa: developing the first compact and cost-effective European Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) for space applications
Eurisa aims at developing a European compact, performant and cost-effective IMU to ensure European non-dependence on critical equipment for space.
Upcoming events
There are no upcoming events to display.